Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that occurs at a specific time of year, typically in the winter months when daylight hours are shorter. The seasonal affective disorder symptoms often overlap with those of regular depression, including persistent low mood, lack of energy, changes in sleeping and eating patterns, and difficulty concentrating. Interestingly, certain individuals also experience these symptoms during summer, albeit less commonly.
What are the causes of SAD? The precise causes remain unclear, but it’s thought to be related to changes in sunlight exposure. Reduced daylight can affect the body’s internal clock and the regulation of mood-related neurotransmitters, such as serotonin. Furthermore, changes in melatonin levels, which influence sleep patterns and mood, may also contribute.
Also to see : Enhancing stability and agility: discover the benefits of regular tai chi for seniors
Mental health seasonal changes significantly impact those with SAD, highlighting the importance of recognising symptoms early. Ensuring ample exposure to natural light, maintaining a routine, and seeking professional advice when necessary can mitigate these effects. Understanding SAD’s link to mental health and seasonal cycles offers insight into managing this condition effectively. Such comprehension is crucial for implementing appropriate interventions and lifestyle adaptations to improve well-being.
The Science Behind Essential Oils
Exploring the benefits of essential oils can offer intriguing insights into mental wellbeing. These natural extracts, derived from plants, have garnered attention for their potential therapeutic effects. Whether through inhalation or topical application, essential oils can impact the human mood by interacting with brain pathways linked to emotion and stress.
Also read : Tailoring your diet: unlocking the power of nutrigenomics for managing metabolic syndrome
Aromatherapy Explained
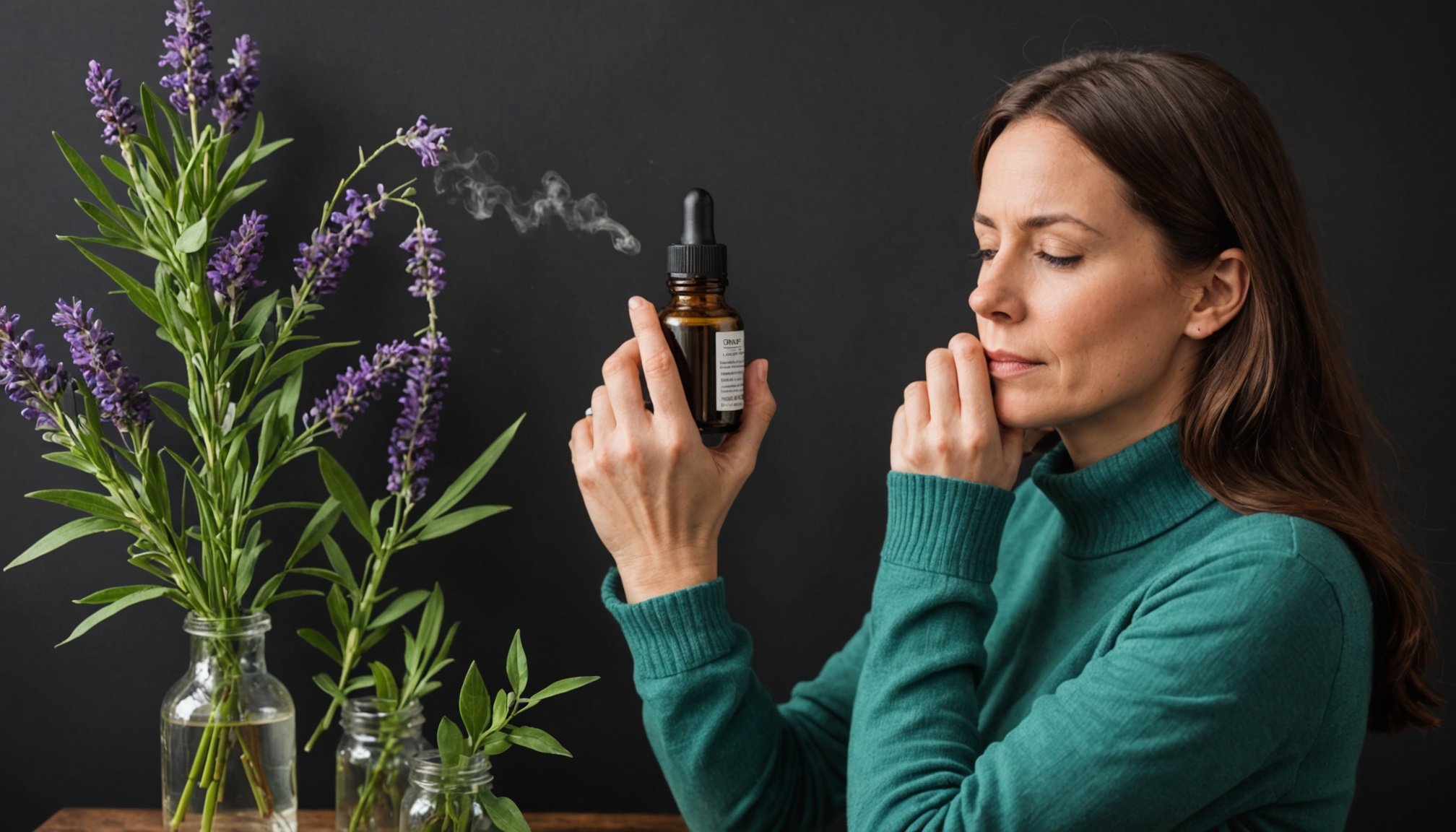
Aromatherapy is a practice that utilises essential oils for therapeutic purposes. It operates on the principle that scents can alter psychological or physiological states. Scientific studies support the efficacy of essential oils in mood enhancement, suggesting they might influence neurotransmitter activities. For instance, lavender essential oil is known for its calming effect, potentially due to its interaction with neurotransmitters that regulate anxiety.
Therapeutic effects vary among different oils. Certain essential oils, such as bergamot and chamomile, are credited with reducing stress and promoting relaxation. The key lies in their unique aromatic compounds. It’s important to choose oils tailored to individual needs to optimise their potential benefits. As more research unfolds, the role of essential oils in mental health, including their application in tackling Seasonal Affective Disorder, continues to capture the curiosity of both researchers and the public.
Essential Oils for Relieving SAD Symptoms
Exploring essential oils for SAD offers a natural pathway to mood enhancement. Certain oils, such as lavender and bergamot, are renowned for their soothing qualities. These mood-enhancing oils may offer relief by influencing neurotransmitter pathways linked to emotions. Top oils include:
- Lavender: Known for its calming properties, lavender essential oil can reduce anxiety and promote relaxation, crucial for those experiencing seasonal affective disorder symptoms.
- Bergamot: This citrus oil is noted for its uplifting scent. It helps alleviate feelings of sadness and enhances mood.
The mechanisms of action for these oils aren’t entirely understood but are believed to involve interaction with the limbic system, a brain area crucial for emotion regulation. To utilise these benefits, consider diffusion or topical application. Diffusion releases the oil’s aroma into the air, creating an uplifting atmosphere. For topical use, dilute essential oils with a carrier oil to prevent skin irritation and apply to pulse points like the wrists.
Always adhere to recommended dosages to prevent adverse effects. Incorporating these oils thoughtfully into one’s daily routine may help alleviate the mental health challenges accompanying seasonal changes.
Integrating Essential Oils into Daily Life
Incorporating essential oils into your daily routine can be a simple yet effective way to enhance well-being. Practical tips involve selecting oils that resonate with personal preferences and needs. To create an uplifting environment, use a diffuser to disperse the aroma throughout a room, transforming the atmosphere with ease.
For those seeking routine enhancement, essential oils can be integrated effortlessly. Establish a schedule for regular use, such as during meditation, to maximise their potential benefits. Consistency in application ensures lasting effects on mood and overall mental health.
Applying oils topically can be part of this routine. Remember to dilute them with a carrier oil to avoid irritation. Pulse points, like wrists and neck, are optimal locations due to their warmth, which aids in scent diffusion.
Finally, the duration of use plays a critical role in effectiveness. Initial daily usage for about two weeks can establish noticeable mood changes. As results manifest, adjust the frequency based on personal response. This adaptable approach not only makes using essential oils sustainable but also enhances everyday life by nurturing mental resilience.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
When exploring the use of essential oils, it’s vital to be aware of potential side effects and contraindications. Though generally safe, some may experience allergic reactions, skin irritation, or respiratory issues upon exposure. To mitigate these risks, always perform a patch test before broad application. Apply a small amount of diluted essential oil to the inner forearm and wait 24 hours, observing any reaction.
While essential oils offer numerous benefits, they are not universally suitable. Certain populations, including pregnant women, children, and individuals with specific health conditions, should proceed with caution. Some essential oils, like wintergreen or clary sage, may interact with medications or exacerbate pre-existing health issues.
Consulting healthcare providers is essential, particularly for those with underlying conditions. Their expertise ensures that essential oil use complements existing treatments without introducing adverse interactions.
To ensure essential oils safety, follow recommended dilution ratios and application methods. Overuse or improper application can lead to unforeseen complications. Prioritising safety and informed use empowers individuals to harness the therapeutic potential of essential oils while safeguarding their well-being.
Alternative Therapies for SAD
Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) can be managed through a variety of other SAD treatments. Light therapy, for instance, involves exposure to a light box that mimics natural sunlight, helping regulate mood by affecting serotonin and melatonin levels. Users typically sit near the box for 20-30 minutes each day, preferably in the morning. This method is rooted in the understanding that decreased daylight during winter months can disrupt circadian rhythms, contributing to SAD symptoms.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is another effective approach. By focusing on altering negative thought patterns and behaviours, CBT helps patients develop coping strategies to address the emotional aspects of SAD. Structured sessions with a trained therapist can lead to significant improvements in mood and overall mental well-being.
Exploring these therapies alongside essential oils offers a comprehensive approach to managing SAD. While essential oils can enhance mood through their therapeutic effects, treatments like light therapy and CBT address underlying physiological and psychological causes. It’s crucial to find a balance that works for the individual, as the effectiveness of these interventions can vary. This personalised strategy provides a more robust defence against the challenges posed by seasonal changes.